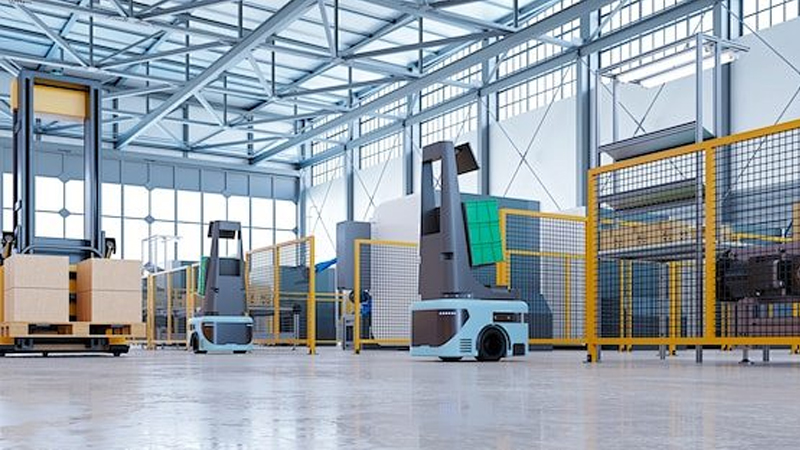
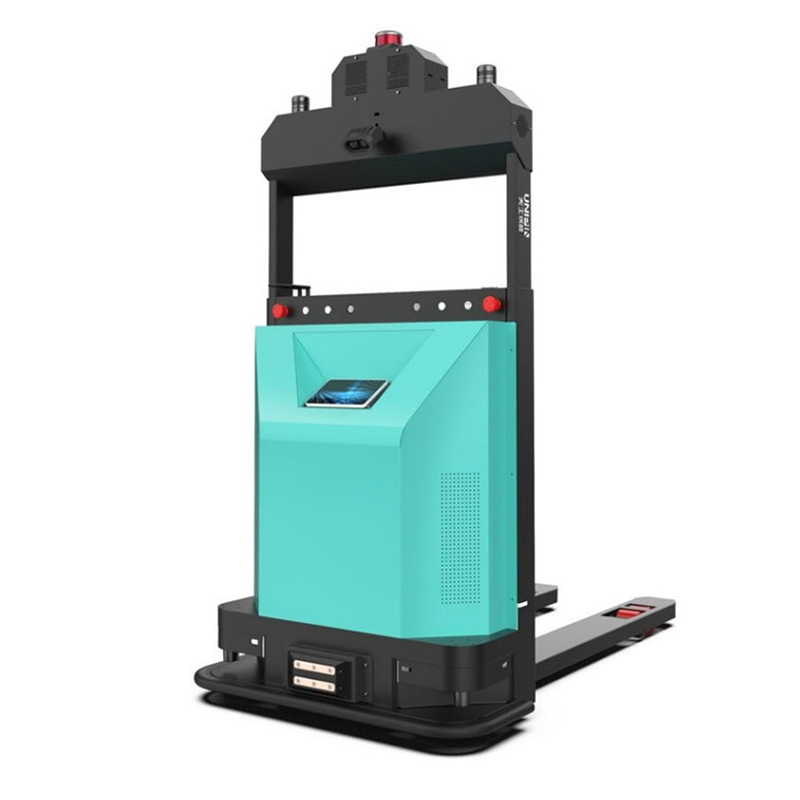
Working principle of intelligent unmanned forklift
1. Path planning: Before moving goods, intelligent unmanned forklifts need to plan their path through a controller according to the requirements of the moving task. The factors considered in path planning include the size, shape, weight, etc. of the goods, as well as the vehicle's endurance and handling time.
2. Autonomous navigation: Intelligent unmanned forklifts collect environmental information through sensors (such as LiDAR, cameras, etc.), and after processing, recognize the characteristics of the surrounding environment to achieve autonomous navigation. Through the data collected by sensors, vehicles can obtain real-time information on their own position and posture, as well as information on the position and distance of surrounding obstacles.
3. Automatic control: The intelligent unmanned forklift precisely controls the vehicle through a controller, achieving functions such as automatic steering and lifting. The controller achieves precise control of the vehicle by processing and analyzing the data collected by sensors, as well as preset control strategies and algorithms.
4. Cargo handling: Based on path planning and autonomous navigation, the intelligent unmanned forklift reaches the designated position and places the cargo at the target position by adjusting the lifting and forward/backward tilting angles of the cargo loading device. During the transportation process, the vehicle will adjust according to the shape and size of the goods to ensure their stability and safety.
5. Real time monitoring and adjustment: During the transportation process, operators can monitor the working status and transportation situation of the vehicle in real time through the human-computer interaction interface. If necessary, the vehicle can be manually controlled or the transportation strategy can be adjusted. At the same time, the vehicle will also make adaptive adjustments according to the actual situation to adapt to different handling scenarios and needs.